ZATH Brand Cervical Interbody Cage PEEK Cage Factory CE ISO
ZATH Brand Cervical Interbody Cage PEEK Cage Factory CE ISO
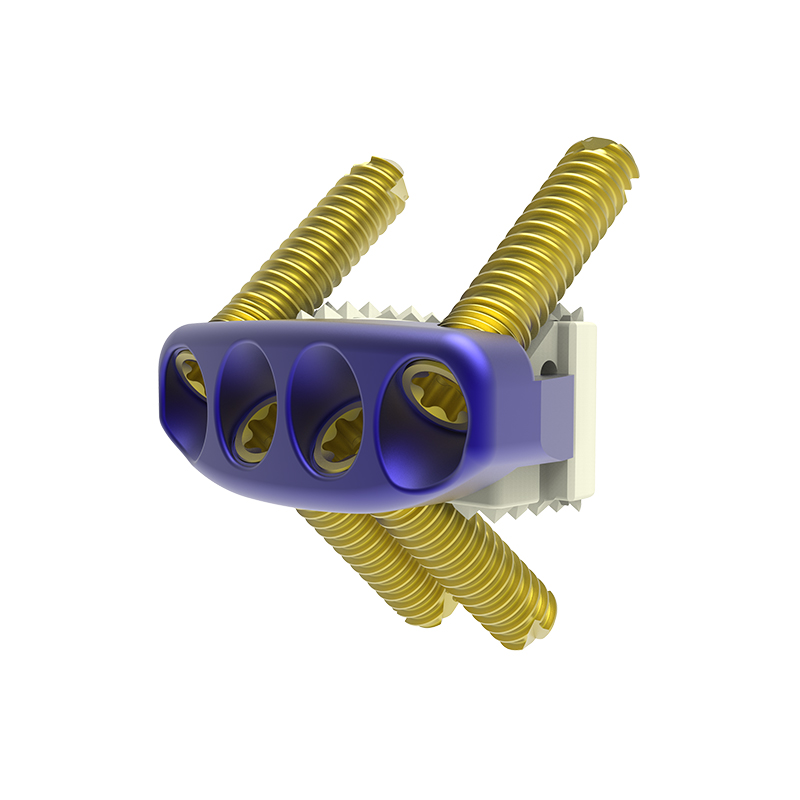
Product Description
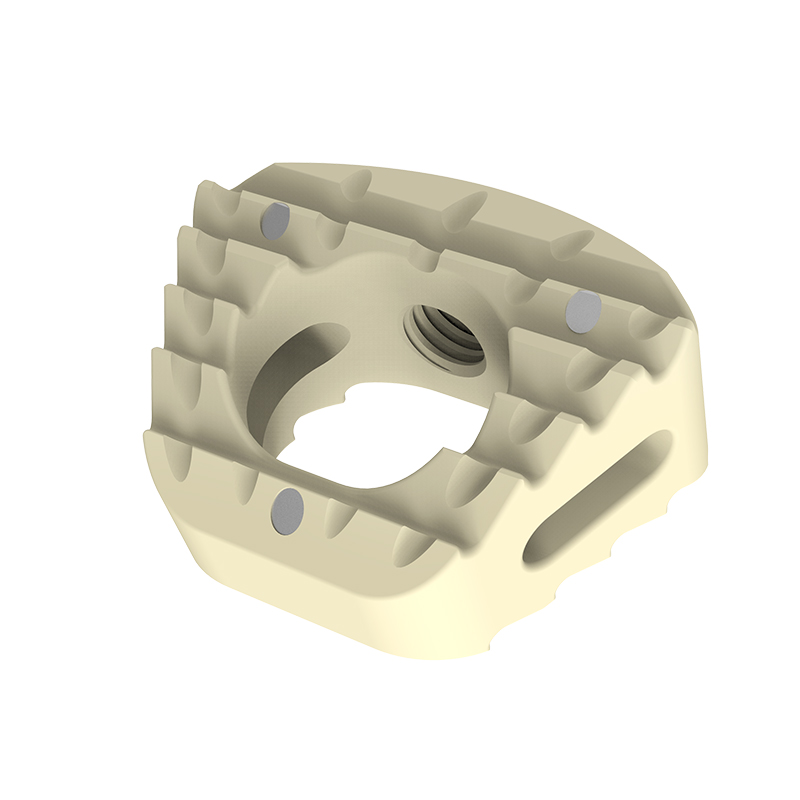
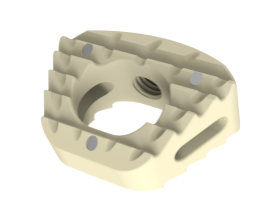
Tantalum Markers
Allow for visualization and implant placement verification.
Pyramidal Teeth
Prevent implant migration
Large Center Opening
Allows more area for bone graft-to-endplate contact

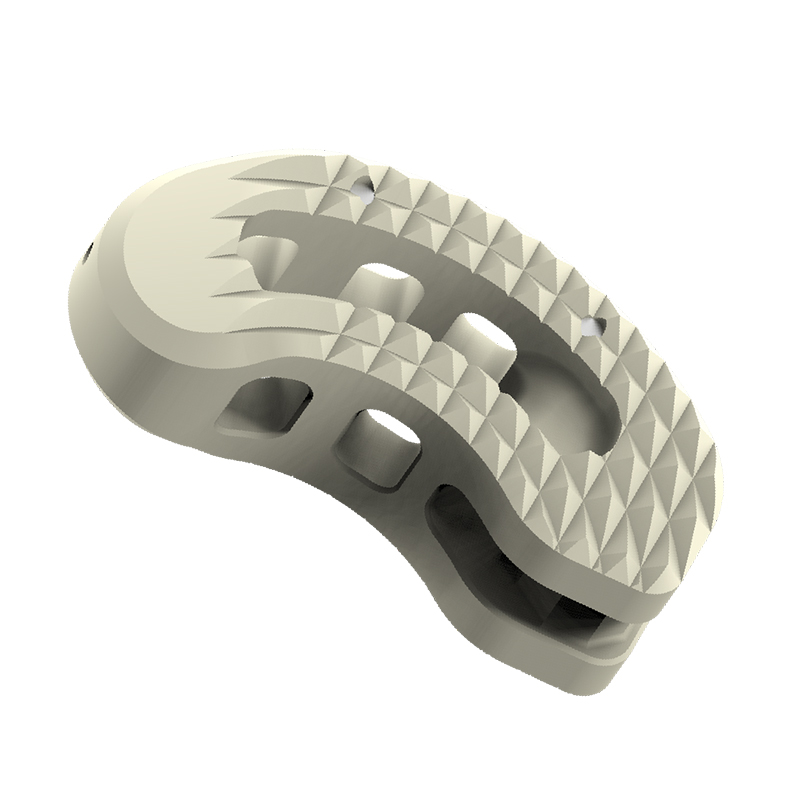
Trapezoid Anatomical Shape
To achieve proper sagittal alignment
Lateral Openings
Facilitates vascularization
Anatomic Sagittal Profile
Disperse stress to maintain the interbody balance
Restore cervical normal lordosis
Reduce the damage to vertebral anterior edge during implanting
The anatomic design reduce the risk of prolapse

Convex

Conraindications
There are several contraindications to consider before undergoing Cervical Interbody Cage (CIC) placement. These contraindications may include:Active infection or systemic infections: Patients who have active infections, such as osteomyelitis or sepsis, are usually not suitable candidates for CIC placement. This is because the procedure may introduce bacteria or other pathogens into the surgical site, leading to further complications.Severe osteoporosis: Patients with severe osteoporosis, which is a condition characterized by low bone density and increased risk of fractures, may not be suitable candidates for CIC placement. The weakened bone structure may not provide enough support for the cage, increasing the risk of implant failure.Allergy or sensitivity to implant materials: Some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to certain implant materials, such as titanium or polyetheretherketone (PEEK). In such cases, CIC placement may not be recommended, and alternative treatment options should be considered.Unrealistic patient expectations: Patients with unrealistic expectations or those who are not committed to post-operative care and rehabilitation may not be suitable candidates for CIC placement. It is important for patients to have a clear understanding of the procedure, its potential outcomes, and the required recovery process.Insufficient bone quality or quantity: In some cases, the patient may have insufficient bone quality or quantity in the cervical spine region, which may make CIC placement challenging or less effective. In such cases, alternative treatment options, such as anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) or posterior cervical fusion, may be considered.It is important to note that these contraindications may vary depending on the individual patient and their specific medical condition. It is always best to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the suitability of CIC placement based on the patient's unique circumstances.