For patients who are about to have a hip replacement or are considering a hip replacement in the future, there are many important decisions to make. A key decision is the choice of prosthetic supporting surface for joint replacement: metal-on-metal, metal-on-polyethylene, ceramic-on-polyethylene, or ceramic-on-ceramic. Sometimes, this can be a dilemma!
Total hip replacement surgery can be used to replace an arthritic hip joint, using an artificial joint prosthesis to eliminate pain caused by rubbing surfaces.
Artificial joint prostheses are designed to provide patients with greater stability and minimal wear and tear. Traditional metal and polyethylene implants have been used since the 1960s, but advances in technology have led to ceramic and other materials becoming increasingly popular.
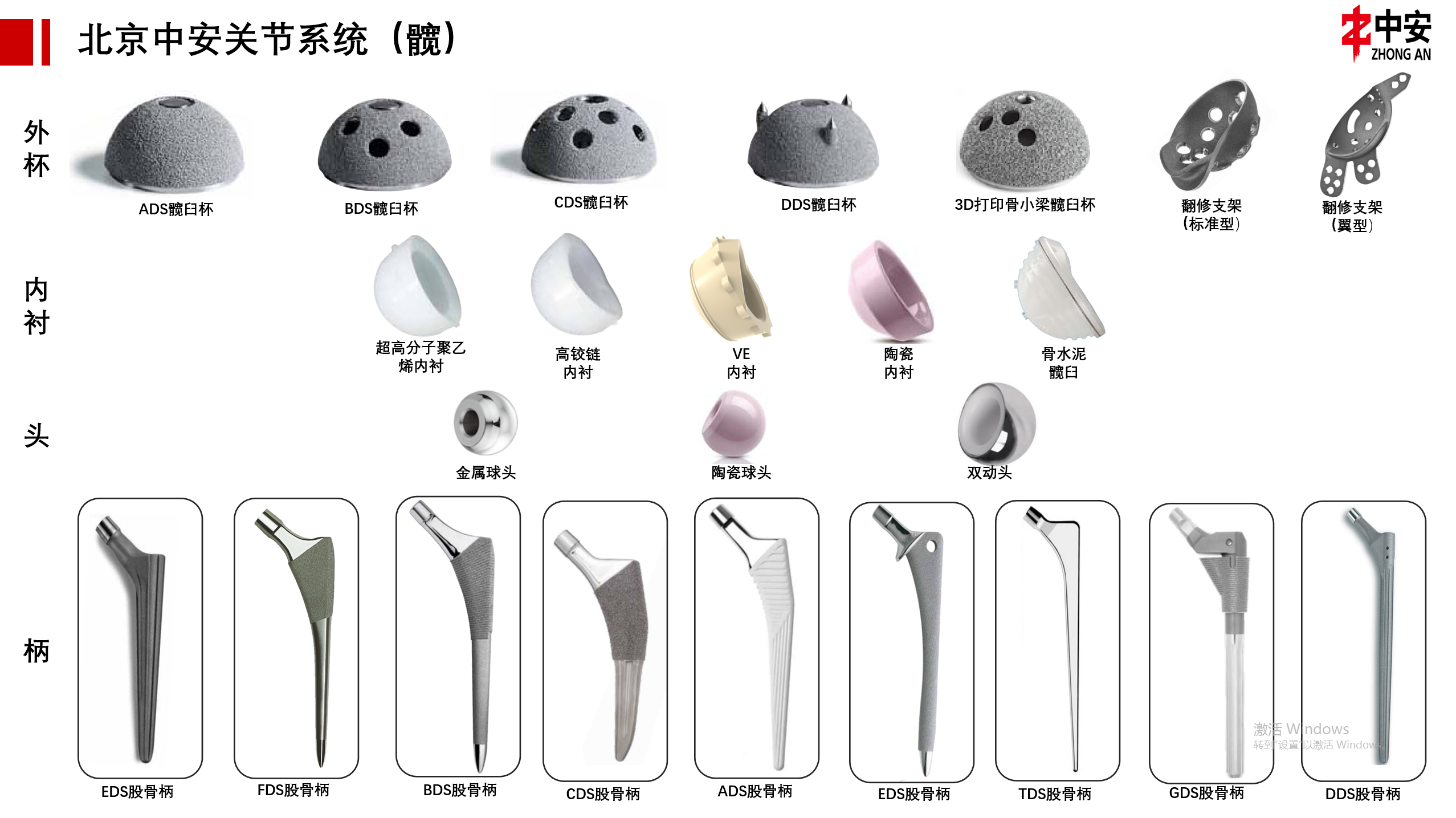
Hip joint replacement implant materials
One of the most common problems after hip replacement is the wear and tear of the joint prosthesis from normal use. Depending on the patient's specific circumstances, such as age, size, activity level, and the surgeon's experience with the specific implant, a hip replacement prosthesis may be made of metal, polyethylene (plastic), or ceramic. For example, if the patient is very active or relatively young and requires a high level of mobility after surgery, the orthopedic surgeon may recommend a ceramic hip implant.
1、Metal ball head and polyethylene (plastic) lining.
Standard metal balls and polyethylene cup liners have been in use since the early 1960s. Scientific research shows that the use of improved polyethylene liners, known as "highly cross-linked" polyethylene liners, can significantly reduce the overall wear rate of implants. Due to its durability and other related properties, metallic polyethylene has been the material of choice for orthopedic surgeons for artificial hip components since the first hip replacement surgeries were performed. The metal ball is made of cobalt-chromium alloy and the lining is made of polyethylene.
2、Ceramic ball head and polyethylene (plastic) lining
Ceramic tips are harder than metal and are the most scratch-resistant implant material. Ceramics currently used in joint replacement surgeries have hard, scratch-resistant, ultra-smooth surfaces that can significantly reduce the wear rate of polyethylene friction interfaces. The potential wear rate of this implant is lower than the potential wear rate of metal on polyethylene.
3、Metal ball head and metal liner
Metal-on-metal friction interfaces (cobalt-chromium alloys, sometimes stainless steel) have been used as early as 1955, but were not approved by the FDA for use in the United States until 1999. As technology advances, wear is significantly reduced, resulting in less inflammation and bone loss. Metal bearings are available in a variety of sizes (ranging from 28mm to 60mm), as well as a variety of neck length options. However, long-term postoperative reports indicate that metal, as a relatively active ion, accumulates metal debris due to long-term wear and tear, which can lead to bone dissolution around the joint prosthesis, ultimately leading to loosening and deformation of the joint prosthesis. The operation failed.
4、Ceramic ball head and ceramic lining
In these hips, traditional metal balls and polyethylene liners have been replaced by high-strength ceramics, which are known for their ultra-low-wear properties. However, while having the advantages of high quality and low wear, they also inevitably have the disadvantage of high cost.
The final choice of implant will be determined based on the patient's specific health factors and will also require the orthopedic surgeon's expertise, education, and expertise to customize a specific manufacturer's product. Therefore, it is necessary to discuss with your orthopedic surgeon before surgery to understand the type of implant they intend to use for your hip replacement surgery, and the reasons for selecting a specific implant.
Post time: Jan-18-2024
