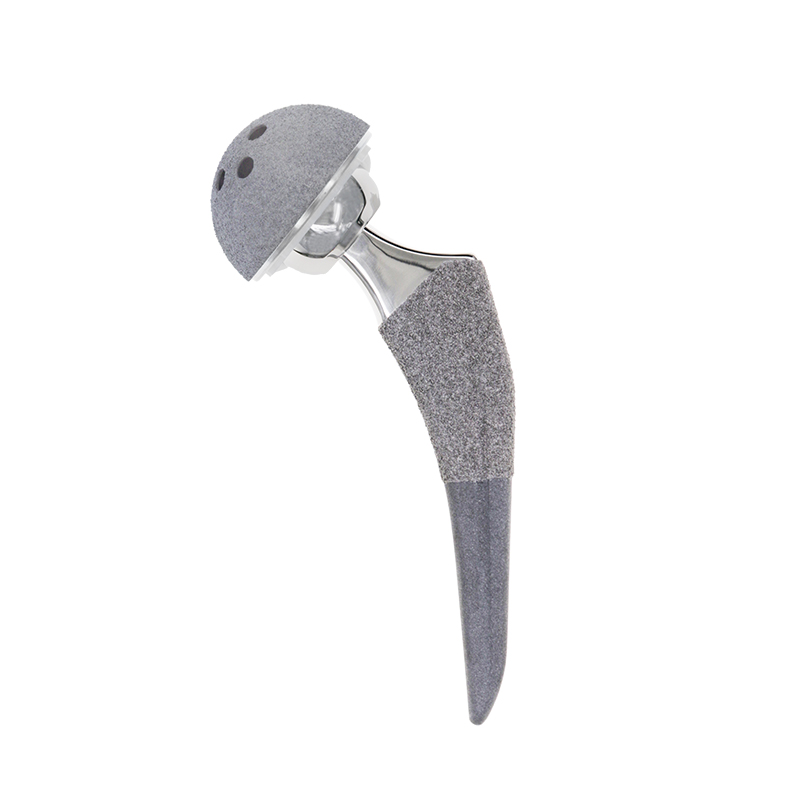
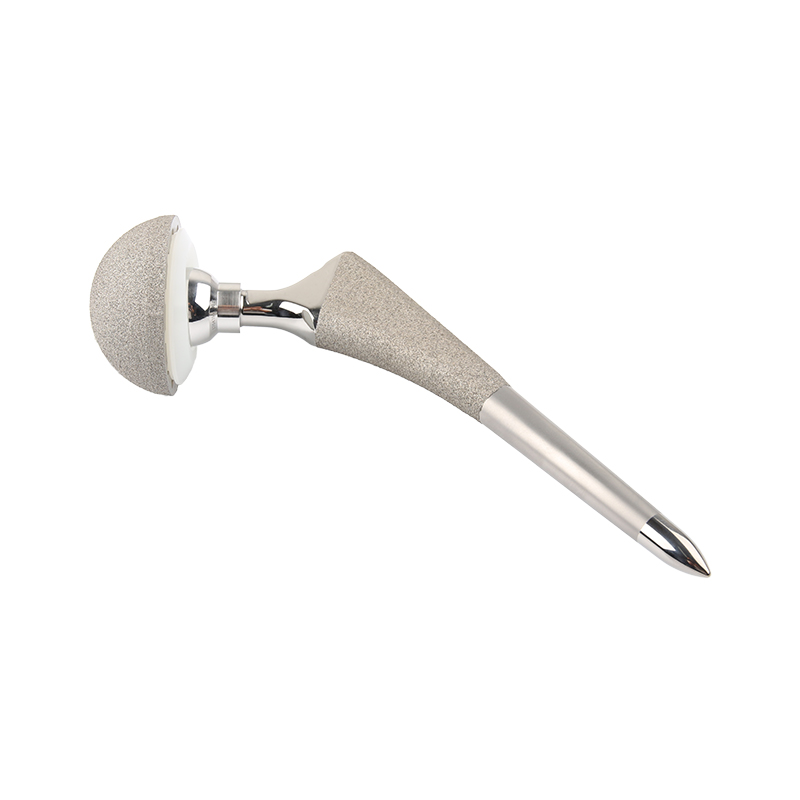
Hot sale Ti alloy JDS total hip replacement titanium joint prosthesis
Product Description

132° CDA
Closer to natural anatomical structure
50° Osteotomy angle
Protect the femoral calcar for more proximal support


Tapered Neck
Reduce the impact during activity and increase range of motion
Reduced lateral shoulder
Protect the greater trochanter and allow minimally invasive surgery


Reduce distal M/L size
Provide proximal cortical contact for A Shape femur to increase initial stability
Groove design on both sides
Beneficial to retain more bone mass and intramedullary blood supply in the AP sides of the femoral stem and enhance the stability of rotation


Proximal lateral rectangular design
Increase antirotation stability.

Curved Distal
Beneficial to implant prosthesis through anterior and anterolateral approaches, while avoiding distal stress concentration
Higher roughness for immediate postoperative stability
Larger coating thickness and higher porosity make bone tissue grow deeper into the coating, and also have good long-term stability.
● Proximal 500 μm thickness
● 60% porosity
● Roughness: Rt 300-600μm

Hip joint prosthesis
A hip implant is a medical device used to replace a damaged or diseased hip joint, relieve pain and restore mobility. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the femur (thigh bone) to the pelvis, allowing for a wide range of motion. However, conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, fractures or avascular necrosis can cause the joint to deteriorate significantly, leading to chronic pain and limited mobility. In these cases, a hip implant may be recommended.
From 2012-2018, there are 1,525,435 cases of primary and revision hip and knee joint replacement, among of which primary knee accounts for 54.5%, and primary hip occupies 32.7%.
After the joint replacement, the incidence rate of periprosthetic fracture:
Primary THA: 0.1~18%, higher after revision
Primary TKA: 0.3~5.5%, 30% after revision
There are two main types of hip implants: total hip replacement and partial hip replacement. A total hip replacement involves replacing both the acetabulum (socket) and the femoral head (ball), while a partial hip replacement typically replaces only the femoral head. The choice between the two depends on the extent of the injury and the specific needs of the patient. Recovery after hip implant surgery varies, but most patients can begin physical therapy soon after surgery to strengthen surrounding muscles and improve mobility. With advances in surgical techniques and implant technology, many people experience a significant improvement in their quality of life after hip implant surgery, allowing them to return to their favorite activities with renewed vigor.
hip replacement Clinical Application

joint hip replacement Details
| Stem Length | 110mm/112mm/114mm/116mm/120mm/122mm/124mm/126mm/129mm/131mm |
| Distal Width | 7.4mm/8.3mm/10.7mm/11.2mm/12.7mm/13.0mm/14.8mm/15.3mm/17.2mm/17.7mm |
| Cervical Length | 31.0mm/35.0mm/36.0mm/37.5mm/39.5mm/41.5mm |
| Offset | 37.0mm/40.0mm/40.5mm/41.0mm/41.5mm/42.0mm/43.5mm/46.5mm/47.5mm/48.0mm |
| Material | Titanium Alloy |
| Surface Treatment | Ti Powder Plasma Spray |