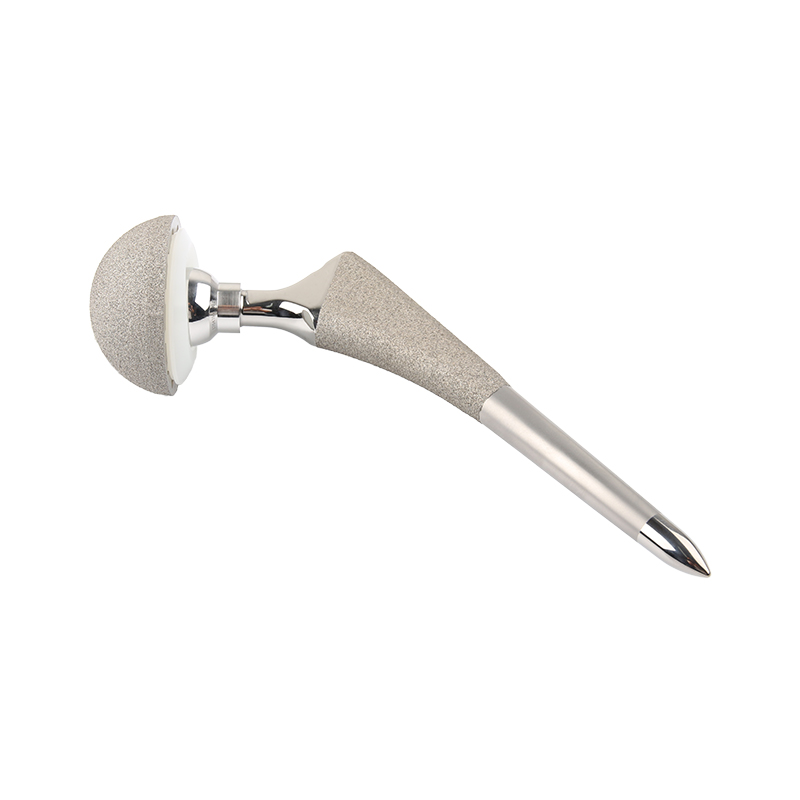
FDS total hip joint implant bipolar
Product Description
● Standard 12/14 taper
● The offset increases gradually
● 130° CDA
● Short and straight stem body

Proximal part with TiGrow technology is conducive to bone ingrowth and long-term stability.
The middle part adopts traditional sand blasting technology and rough surface treatment to facilitate the balanced transmission of the force on the femoral stem.
Distal high polish bullet design reduces cortical bone impact and thigh pain.

Tapered neck shape to increase range of motion

● Oval + Trapezoidal Cross Section
● Axial and Rotational Stability

Double taper design provides
three-dimensional stability

hip joint prosthesis Indications
Total hip replacement, commonly called hip replacement surgery, is a surgical procedure that replaces a damaged or diseased hip joint with an artificial implant. The goal of this surgery is to relieve pain and improve the function of the hip joint.
During surgery, the damaged portion of the hip joint, including the femoral head and acetabulum, is removed and replaced with prosthetic components made of metal, plastic, or ceramic. The type of implant used may vary based on factors such as the patient's age, health, and surgeon preference.
A hip prosthesis is a medical device used to replace a damaged or diseased hip joint, relieve pain and restore mobility. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint that connects the femur (thigh bone) to the pelvis, allowing for a wide range of motion. However, conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, fractures or avascular necrosis can cause the joint to deteriorate significantly, leading to chronic pain and limited mobility. In these cases, a hip implant may be recommended.
Most patients are able to return to normal activities, such as walking and climbing stairs, within a few weeks to months after surgery. Like any surgical procedure, total hip replacement carries certain risks and complications, including infection, blood clots, loose or dislocated implants, nerve or blood vessel damage, and joint stiffness or instability. However, these complications are relatively rare and can usually be managed with proper medical care. Be sure to consult with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to determine whether total hip replacement is the right treatment option for your specific situation and to discuss any questions or concerns you may have.
Clinical Application

hip prosthesys Details
FDS total hip joint implant bipolar
| Stem Length | 142.5mm/148.0mm/153.5mm/159.0mm/164.5mm/170.0mm/175.5mm/181.0mm |
| Distal Diameter | 6.6mm/7.4mm/8.2mm/9.0mm/10.0mm/10.6mm/11.4mm/12.2mm |
| Cervical Length | 35.4mm/36.4mm/37.4mm/38.4mm/39.4mm/40.4mm/41.4mm/42.4mm |
| Offset | 39.75mm/40.75mm/41.75mm/42.75mm/43.75mm/44.75mm/45.75mm/46.75mm |
| Material | Titanium Alloy |
| Surface Treatment | Proximal Part: Ti Powder Spray |
| Medial Part | Carborundum Blasted Coating |
What Is Hip Joint Replacement?
There are two main types of hip implants: total hip replacement and partial hip replacement. A total hip replacement involves replacing both the acetabulum (socket) and the femoral head (ball), while a partial hip replacement typically replaces only the femoral head. The choice between the two depends on the extent of the injury and the specific needs of the patient.
A typical hip implant consists of three main components: the femoral stem, the acetabular component, and the femoral head.

Hip Joint Implant Specification
| Material | Surface Coating | ||
| Femoral Stem | FDS Cementless Stem | Ti Alloy | Proximal Part: Ti Powder Spray |
| ADS Cementless Stem | Ti Alloy | Ti Powder Spray | |
| JDS Cementless Stem | Ti Alloy | Ti Powder Spray | |
| TDS Cemented Stem | Ti Alloy | Mirror Polishing | |
| DDS Cementless Revision Stem | Ti Alloy | Carborundum Blasted Spray | |
| Tumor Femoral Stem (Customized) | Titanium Alloy | / | |
| Acetabular Components | ADC Acetabular Cup | Titanium | Ti Powder Coating |
| CDC Acetabular Liner | Ceramic | ||
| TDC Cemented Acetabular Cup | UHMWPE | ||
| FDAH Bipolar Acetabular Cup | Co-Cr-Mo Alloy & UHMWPE | ||
| Femoral Head | FDH Femoral Head | Co-Cr-Mo Alloy | |
| CDH Femoral Head | Ceramics |
Hip Joint Prosthesis Femoral Stem

Acetabular Components

Femoral Head