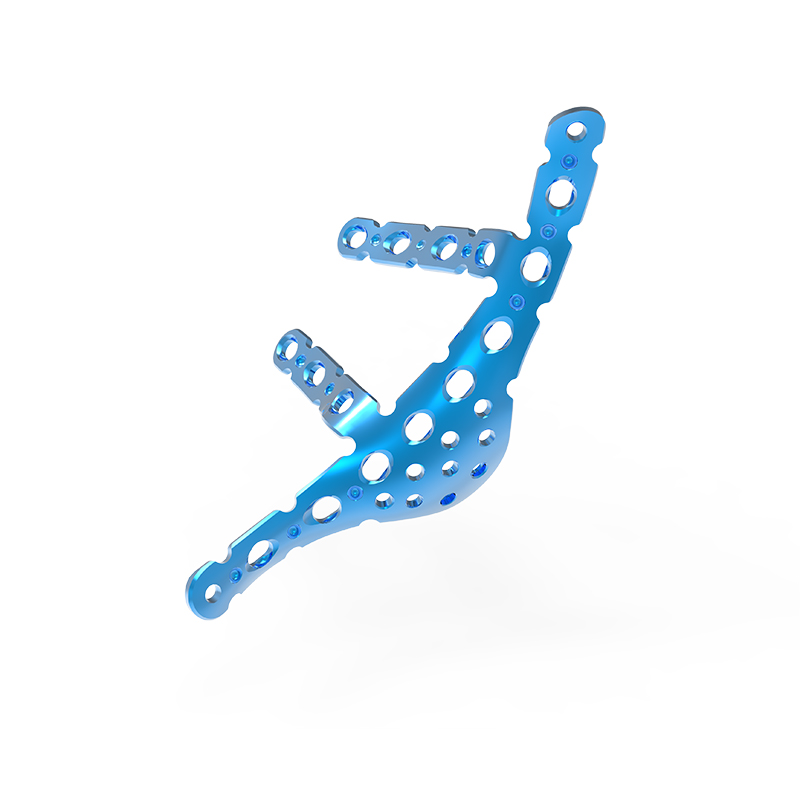
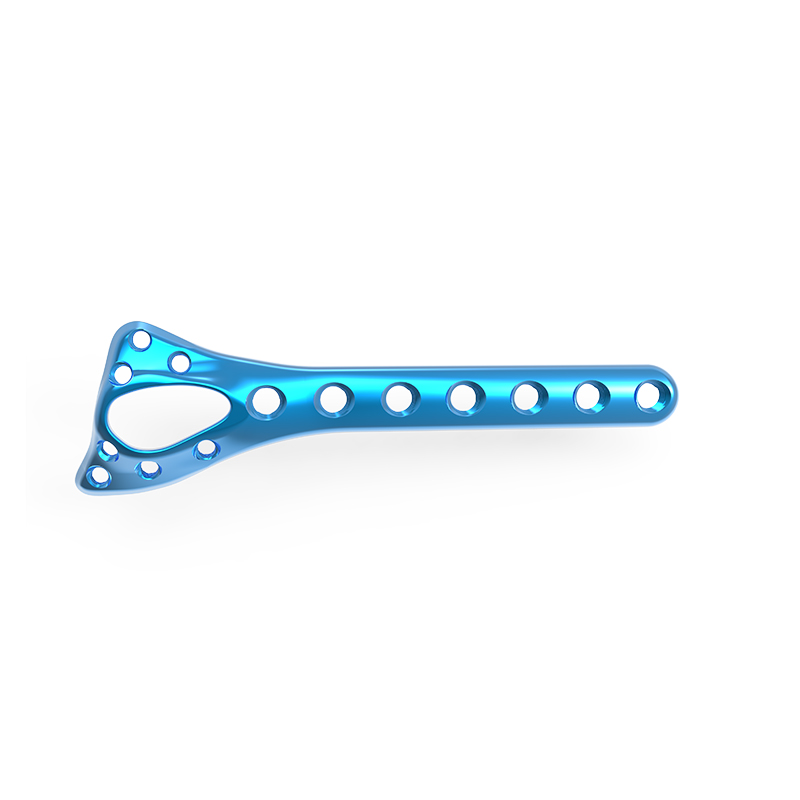
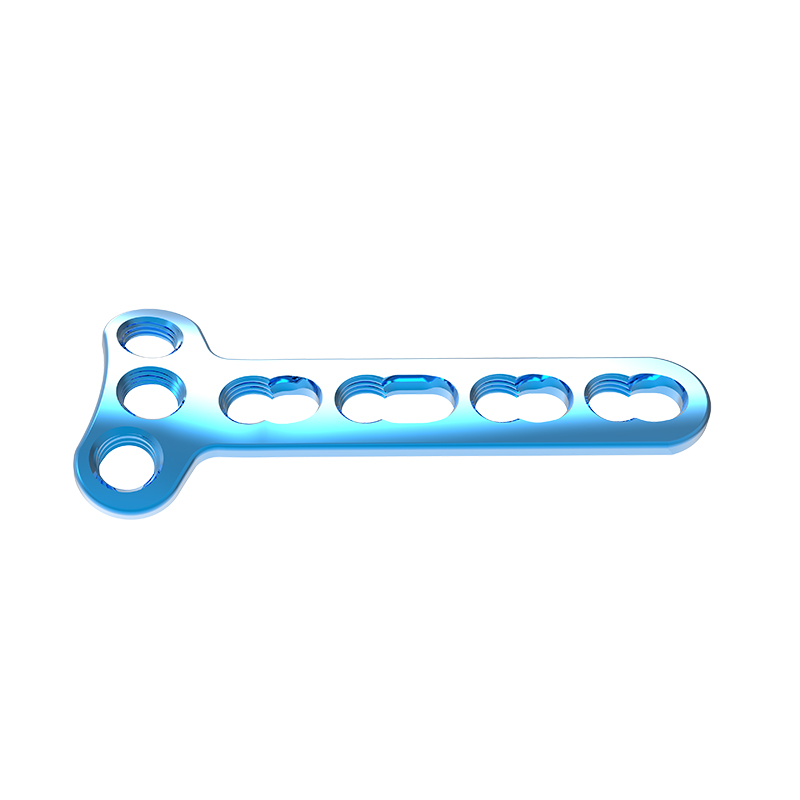
Distal Medial Humerus Locking Compression Plate
Product Features
Two-plate technique for distal humerus fractures
Increased stability can be gained from two-plate fixation of distal humerus fractures. The two-plate construct creates a girder-like structure which strengthens the fixation.1 The posterolateral plate functions as a tension band during elbow flexion, and the medial plate supports the medial side of the distal humerus.


Indications
Indicated for intraarticular fractures of the distal humerus, comminuted supracondylar fractures, osteotomies, and nonunions of the distal humerus.
Product Details
| Distal Medial Humerus Locking Compression Plate | 4 holes x 60mm (Left) |
| 6 holes x 88mm (Left) | |
| 8 holes x 112mm (Left) | |
| 10 holes x 140mm (Left) | |
| 4 holes x 60mm (Right) | |
| 6 holes x 88mm (Right) | |
| 8 holes x 112mm (Right) | |
| 10 holes x 140mm (Right) | |
| Width | 11.0mm |
| Thickness | 3.0mm |
| Matching Screw | 2.7 Locking Screw for Distal Part
3.5 Locking Screw / 3.5 Cortical Screw / 4.0 Cancellous Screw for Shaft Part |
| Material | Titanium |
| Surface Treatment | Micro-arc Oxidation |
| Qualification | CE/ISO13485/NMPA |
| Package | Sterile Packaging 1pcs/package |
| MOQ | 1 Pcs |
| Supply Ability | 1000+Pieces per Month |
I apologize for the confusion earlier. If you are specifically referring to a Distal Medial Humerus Locking Compression Plate operation, it is a surgical procedure used to fix fractures or other injuries in the distal medial region (lower end) of the humerus bone.Here are some key points about the operation:Surgical approach: The operation is usually performed through a small incision made on the inner side (medial) of the arm to access the fractured area.Plate fixation: A locking compression plate is utilized to stabilize the fractured bone fragments. The plate is made of a durable material (usually titanium) and has pre-drilled screw holes. It is fixed to the bone using locking screws, which create a stable construct.Locking screws: These screws are designed to lock into the plate, providing additional stability and preventing back out. They offer resistance to angular and rotational forces, reducing the risk of implant failure and promoting better bone healing.Anatomical contouring: The plate is contoured to match the shape of the distal medial humerus. This allows for a better fit and reduces the need for excessive bending or contouring during the surgery.Load distribution: The locking compression plate helps to distribute the load evenly across the plate and bone interface, decreasing stress concentration at the fracture site. This can prevent complications such as implant failure or nonunion.Rehabilitation: Following the operation, a period of immobilization and rehabilitation is usually recommended to allow the fracture to heal. Physical therapy may be prescribed to restore range of motion, strength, and function in the arm.It's important to note that the specifics of the operation can vary depending on the individual patient, the nature of the fracture, and the surgeon's preference. It is advisable to consult with an orthopedic surgeon to get a detailed understanding of the procedure, potential risks, and the expected recovery process for your specific case.