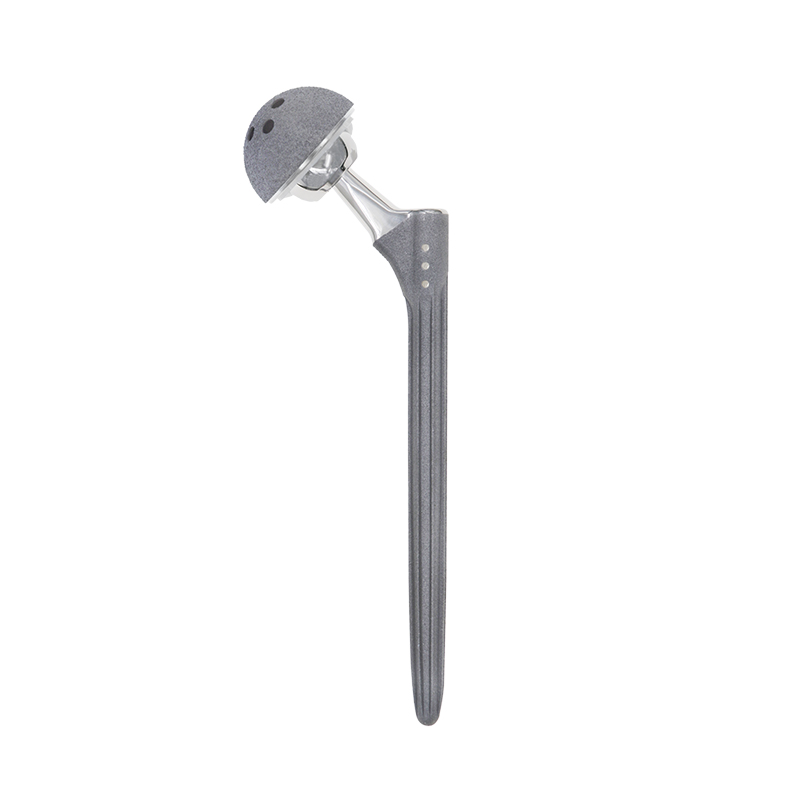
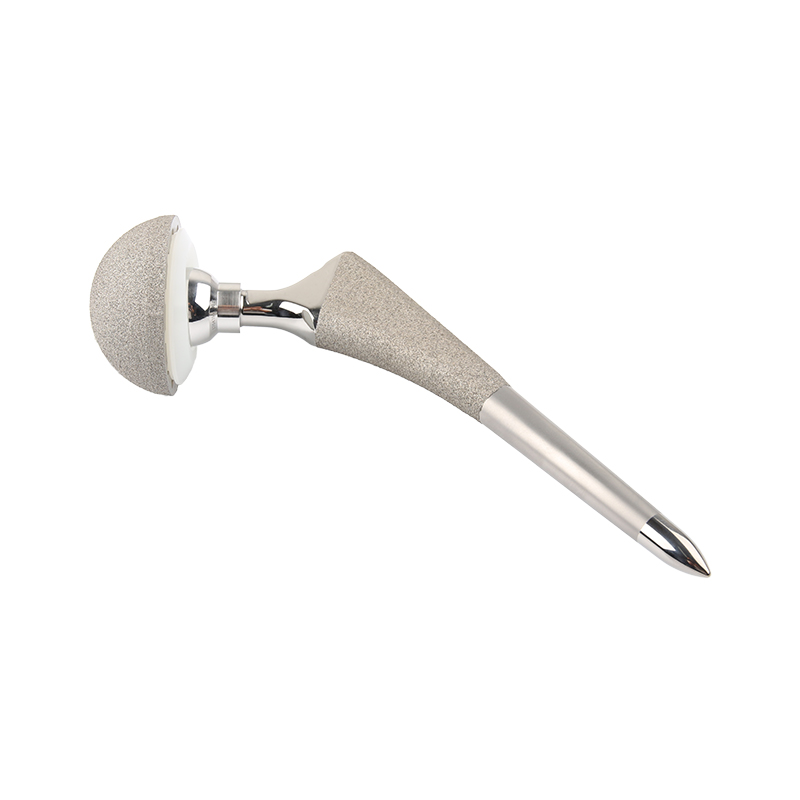
Best selling DDS titanium hip and joint implant prosthesis
Indications
● Primary artificial hip replacement
● Proximal femur deformity
● Proximal femur fracture
● Osteosclerosis of the proximal femur
● Proximal femoral bone loss
● Revision artificial hip joint replacement
● Periprosthetic femoral fractures
● Prosthetic loosening
● Infections is controlled after replacement
Design Principle
The design principles for DDS cementless revision stems are focused on achieving long-term stability, fixation, and bone ingrowth. Here are some key design principles:
Porous Coating: Cementless revision stems typically have a porous coating on the surface that comes in contact with the bone. This porous coating allows for enhanced bone ingrowth and mechanical interlocking between the implant and the bone. The type and structure of the porous coating can vary, but the goal is to provide a rough surface that promotes osseointegration.
Modular Design: Revision stems often have a modular design to accommodate various patient anatomies and allow for intraoperative adjustments. This modularity allows surgeons to select different stem lengths, offset options, and head sizes to achieve optimal fit and alignment.Enhanced Proximal Fixation:
DDS Cementless revision stems may incorporate features such as flutes, fins, or ribs in the proximal portion to enhance fixation. These features engage with the bone and provide additional stability, preventing implant loosening or micromotion.
total hip implant Clinical Application

hip joint Details
|
DDS Cementless Revision Stem |
13# 190 mm |
|
13# 225 mm |
|
|
14# 190 mm |
|
|
14# 225 mm |
|
|
14# 265 mm |
|
|
15# 190 mm |
|
|
15# 225 mm |
|
|
15# 265 mm |
|
|
16# 190 mm |
|
|
16# 225 mm |
|
|
16# 265 mm |
|
|
17# 225 mm |
|
|
17# 265 mm |
|
|
18# 225 mm |
|
|
18# 265 mm |
|
|
19# 225 mm |
|
|
19# 265 mm |
|
|
Material |
Titanium Alloy |
|
Surface Treatment |
Carborundum Blasted Coating |
|
Qualification |
CE/ISO13485/NMPA |
|
Package |
Sterile Packaging 1pcs/package |
|
MOQ |
1 Pcs |
|
Supply Ability |
1000+Pieces per Month |
Product Description




Indications
Hip joint is a surgical procedure that aims to improve patient mobility and reduce pain by replacing the damaged hip joint with artificial components. It is typically performed when there is evidence of sufficient healthy bone to support and stabilize the implants. THA is recommended for patients suffering from severe hip joint pain and/or disability caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, traumatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and congenital hip dysplasia. It is also indicated for cases of avascular necrosis of the femoral head, acute traumatic fractures of the femoral head or neck, failed previous hip surgeries, and certain instances of ankylosis.Hemi-Hip Arthroplasty, on the other hand, is a surgical option suitable for patients who have a satisfactory natural hip socket (acetabulum) and enough femoral bone to support the femoral stem. This procedure is particularly indicated in specific conditions, including acute fractures of the femoral head or neck that cannot be effectively reduced and treated with internal fixation, fracture dislocations of the hip that cannot be appropriately reduced and treated with internal fixation, avascular necrosis of the femoral head, non-union of femoral neck fractures, certain high subcapital and femoral neck fractures in elderly patients, degenerative arthritis that affects only the femoral head and does not require replacement of the acetabulum, as well as pathologies involving only the femoral head/neck and/or proximal femur that can be adequately addressed through hemi-hip arthroplasty.The decision between Total Hip Arthroplasty and Hemi-Hip Arthroplasty depends on various factors, such as the severity and nature of the hip condition, the age and overall health of the patient, and the surgeon's expertise and preference. Both procedures have demonstrated efficacy in restoring mobility, reducing pain, and improving the quality of life for patients afflicted with different hip joint disorders. It is essential for patients to consult with their orthopedic surgeons to determine the most appropriate surgery option based on their individual circumstances.
Clinical Application

DDS Hip Stem Details
| Stem Length | Distal Diameter | Cervical Length
|
Offset |
| 190mm/225mm | 9.3mm
|
56.6mm | 40.0mm |
| 190mm/225mm/265mm | 10.3mm | 59.4mm | 42.0mm |
| 190mm/225mm/265mm | 11.3mm | 59.4mm | 42.0mm |
| 190mm/225mm/265mm | 12.3mm | 59.4mm | 42.0mm |
| 225mm/265mm | 13.3mm | 59.4mm | 42.0mm |
| 225mm/265mm | 14.3mm | 62.2mm | 44.0mm |
| 225mm/265mm | 15.3mm | 62.2mm | 44.0mm |
Product Description




Hip Joint Indications
Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA) is a surgical procedure that aims to improve patient mobility and reduce pain by replacing the damaged hip joint with artificial components. It is typically performed when there is evidence of sufficient healthy bone to support and stabilize the implants. THA is recommended for patients suffering from severe hip joint pain and/or disability caused by conditions such as osteoarthritis, traumatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and congenital hip dysplasia. It is also indicated for cases of avascular necrosis of the femoral head, acute traumatic fractures of the femoral head or neck, failed previous hip surgeries, and certain instances of ankylosis.Hemi-Hip Arthroplasty, on the other hand, is a surgical option suitable for patients who have a satisfactory natural hip socket (acetabulum) and enough femoral bone to support the femoral stem. This procedure is particularly indicated in specific conditions, including acute fractures of the femoral head or neck that cannot be effectively reduced and treated with internal fixation, fracture dislocations of the hip that cannot be appropriately reduced and treated with internal fixation, avascular necrosis of the femoral head, non-union of femoral neck fractures, certain high subcapital and femoral neck fractures in elderly patients, degenerative arthritis that affects only the femoral head and does not require replacement of the acetabulum, as well as pathologies involving only the femoral head/neck and/or proximal femur that can be adequately addressed through hemi-hip arthroplasty.The decision between Total Hip Arthroplasty and Hemi-Hip Arthroplasty depends on various factors, such as the severity and nature of the hip condition, the age and overall health of the patient, and the surgeon's expertise and preference. Both procedures have demonstrated efficacy in restoring mobility, reducing pain, and improving the quality of life for patients afflicted with different hip joint disorders. It is essential for patients to consult with their orthopedic surgeons to determine the most appropriate surgery option based on their individual circumstances.
Clinical Application